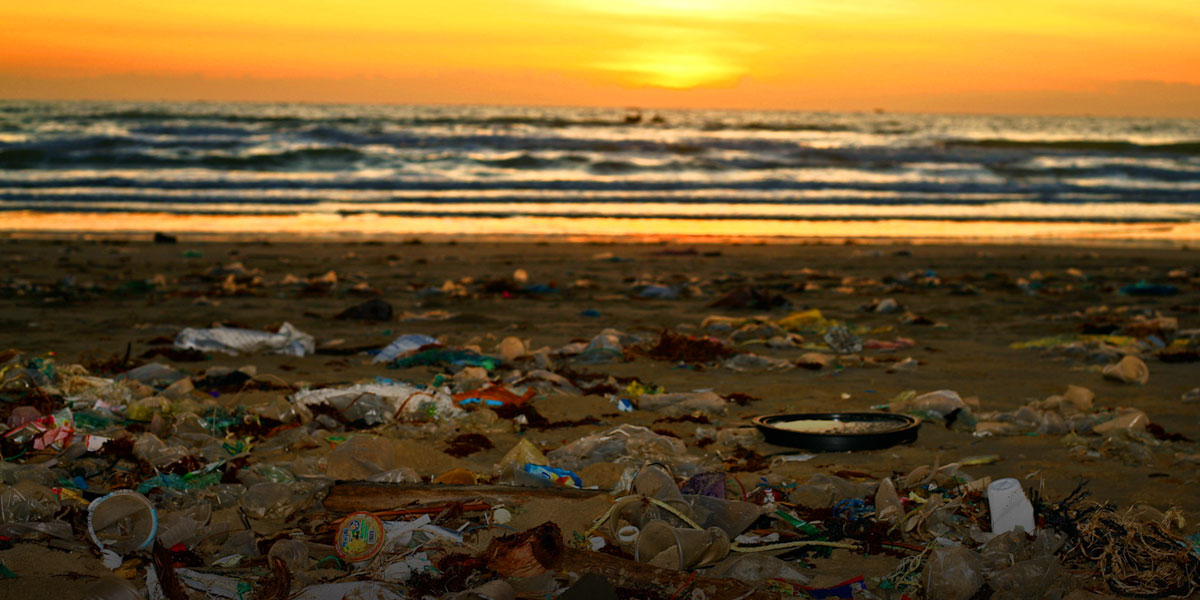

The current increase in the average temperature of the Earth is the result of the human action, through the emission of greenhouse effect gases that alter the natural climate variability. The oceans have had until now a regulatory role in climate through a series of physical, chemical and biological processes that balance natural fluctuations. The pollutant discharges interfere with these processes by altering their natural balance and affecting human health. Policy mitigation and adaptation development scientifically well based is essential for the survival of our planet.
